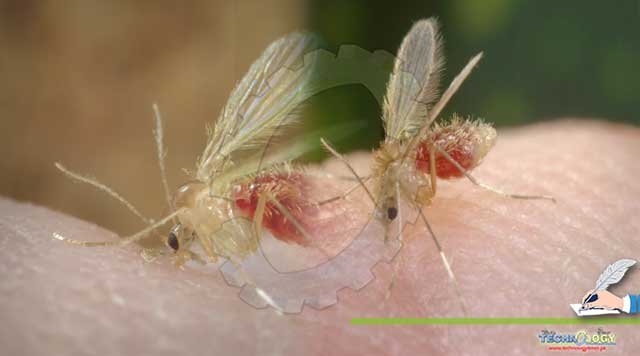
Leishmaniasis is a parasitic disease caused by more than 20 different protozoan species belongs to the genus Leishmaniasis and the family kinetoplastida.
By SAMREEN BAIG
Approximately more than 30 species of Phlebotamine sand fly are responsible for the spread of this disease. This disease is transmitted in humans by the bite of female sand fly.
Leshminiasis shows clinical manifestations which ranges from self-limiting cutaneous to fatal visceral complications depending upon the immune response of the host and the species of Leishmania parasite. For instance, chemotherapeutic agents like N-methyl glucamineantimonate, sodium stibogluconate, Amphotericin B and pentamidine can be administrated through injections because they are not active orally, exorbitant & most importantly these drugs had severe negative effects on renal as well as cardiovascular system.
Leishmaniasis along with malaria are among those diseases which affect the people living in rural areas of the Pakistan. In rural area people are living in unhygenic & socioecnomically poor condition. As a result they areunable to get proper medication. Furthermore , the medicines for the tretment of leshminiasis are very expensive so the people directs rely on herbal medicines. The use of traditional phyto-medicines is very high in Pakistan due to the availability and low cost. The marketed available chemically synthesized drugs for the treatment of leshminiasis are not more effective in treating the disease due to low activity and associates side effects. New ways must sought out to explore efficient drugs for the treatment of leshminiasis.
Plant based natural products have potential in the treatment of several human serious aliments including leshminiasis. Extracts derived from some medicinally important plants have shown positive effects against leshminia promastigotes such as L.Tropica promastigotes.
For instance the plant extracts of Haplophyllum myrtifolium, Arbutus unedo , Hygrophila guianensis Nees have been studied to check the antileishmanial potential in different plant extracts of the above mentioned plants.
Plants contain different types of medicinally active secondary metabolites such as phenolics, flavonoids, alkaloids, tannins and saponins, phenols and terpenoids have reportedly shown to influence higher antileishmanial attributes. Unfortunately, the production yield of these natural products in the plants is low due to certain factors such as geographic variability, types of tissues, physiological status, and environmental conditions. For the effective production and enhancement of the important secondary metabolites, plant cell cultures ensure the production of hygienic, healthy plant germplasm that contain phytochemicaly consistent profiles. Within the different plant cell culture approaches callus and cell suspension cultures, can be manipulated for the production of biomass and enhancement of plant secondary metabolites. Callus culture can be treated with elicitors such as methyl jasmonate in presence of plant growth substance to elicit enhanced production of important metabolites. Methyl jasmonate acting as a signal compounds have been employed in a variety of plant cell cultures. To increment the production of secondary metabolites including saponins, tannins and essential products.
The plants belong to the family Liliaceae and Lamiaceae (Aloe barbadensis, Thuspeinanta brahuica (boiss.) Briq, Neprta praetervisa Rech.f, and Saliva bucharica Popov) were used against leishmaniasis. Ajuga bracteosa from the family Lamiaceae is known for variety of medicinal uses. It is anthelmintic, astringent, antibacterial, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic antitumor, hypoglycemic and it also remediates intestinal ailments and have substantial analgesic properties Ajuga bracteosa contains diverse important compounds such as neo-clerodane diterpenoids, withanolides, iridoid glycosides and phytoecdysteroids. 20-Hydroxyecdysone is a primary bio active constituent of Ajuga bracteosa & it has multiple functions like its strong effects against microbes, cancer and anti-inflammatory properties. Therefore, it is imperative to investigate and explore medicinal plants scientifically for the development of novel anti-leishmanial drugs of strong efficacy.