Livestock or modern dairy farming and beef farming(Fattening) are emerging field of our country and growing day by day but unfortunately echinococcosis is major problem in livestock, As bovine are intermediate host of echinococcus so there is a big loss of livestock in our country due to this disease.
By Dr. Muhammad Rahman,Dr. Muhammad Sohail Sajid,Dr. Hamid Ali Rana
Introduction:
According to census of last decade there is about 2.2% death rate globally due to Echinococcus.
Echinococcosis or Hydatid disease also called as hydatid cyst disease is a disease which can be count in twenty most neglected zoonotic diseases (NZD) in the world and likewise in our country as it can transmit to human from animal via contact. Echinococcus is a zoonotic disease which effect about all living beings i.e Bovine, Ovine, Caprine, Canine, Feline, Equine and Homo sapiens(men) etc. As Pakistan is an agriculture country and more than 60% people belong to this by profession, Livestock play important role in economy of our country and we can say that agriculture and livestock go parallel and are dependant on each other.
Echinococcosis or hydatidosis is a transmissible disease which is brought about by metasestode of tapeworm (the larval phases of taeniid cestodes) of the genus Echinococcus. There are two significant sorts of disease in people that are Cystic Echinococcosis (CE), cause sore in delicate tissues as liver, muscles etc or Hydatidosis and Alveolar Echinococcosis (AE), cause growth type cysts in lungs which is brought about by E.granolosis and E.multilocularis respectively.
Other species of this genus are E. multiocularis, E. vogeli and E. oligarthrus. E. multilocularis causes alveolar echinococcosis which is the development of a tumor like lesion that usually occurs in the liver. Neotropical Echinococcus species i.e., E. vogeli causes polycystic and E. oligarthrus causes rare unicyctic form of disease. There are several genetic strains of E. granulossus reported recently
Pathogenesis:
Disease caused by Taenia echinococcus is due to the larval stage of cestode tapeworm, which is called the Taenia echinococcus, growing inside of people.
Most of the time, the dog is the main host. With use of contaminated, the dog gets sick.lung, liver, and other cyst-producing organs of intermediate hosts, such as sheep. Cysts: These cysts”Water vesicles” have the heads of tapeworms inside.
By the tens of thousands, scolex grow. It turns the dog’s intestines into the adult form.
The cestode is a type of fish. It’s not very big, but the taenia have a lot of small parts.
Size: 4 to 5 mm. Head, neck, and 2 arms body par the head of each one.
The mucosa of the person who is the host. When the last proglottid, which has the sexual organs inside of it, gets bigger, it can’t fit. The ova are shed in the dog’s faeces,so this is where they come from. contaminating grass and water that might be eaten The intermediate host, such as sheep, eats the poison. A lot of people get sick because they touch infected dogs. In rural areas, people can easily become infected with germs.
Transmission:
Echinococcus granulosus necessitates the use of two different types of hosts: a definitive host and an intermediate host. It is thought that dogs serve as the definitive host for this parasite, with sheep serving as the most common intermediate host. However, cattle, goats, horses, pigs, and camels may also serve as intermediate hosts. It is possible for humans to serve as intermediate hosts for E. granulosus; however, this is uncommon, and as a result, humans are regarded as aberrant or abnormal intermediate host. It is important to note that the immunity of both the definitive and intermediate hosts, as well as the contact rate between the intermediate and definitive hosts, play an important role in the transmission of the parasite.
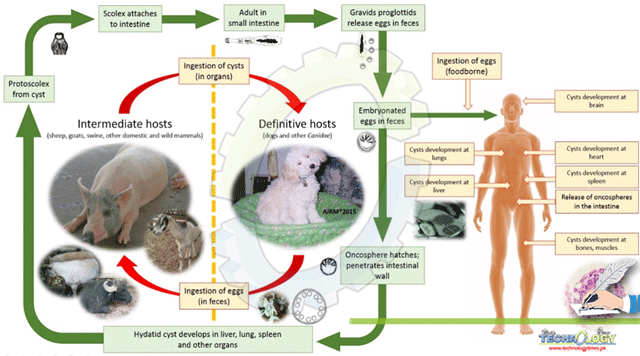
Life cycle:
The developed E. granulosus (about 2–7 mm long) illustration lives inside the intestinal tract of the host. Gravid proglottids make eggs that may pass in faeces, and they spread quickly. After the eggs are ingested by an intermediate host, they hatch in the small intestine and discharge six-hooked stage called oncospheres that infiltrate inside intestinal wall and move through the circulatory system(blood) into different parts of the body, especially the lungs and liver. In such organs, the oncosphere grows into thick walled hydatid cyst that grows, making protoscolices and daughter cysts which fill inside of the cyst. The definitive host gets disease by eating the organs having cysts, of the intermediate host that have been infected with the hydatidosis. protoscolices float away after being eaten. They bind to the intestinal layer and grow to the adult stages with in 31 to 80 days.
Humans are “abnormal intermediate hosts,” and they get infected by eating eggs. Oncospheres that release inside intestine, and hydatid cysts grow in a wide range of organs. If a cyst bursts, the protoscolices that came out may form new cysts in the other parts of the body (secondary echinococcosis).
Clinical signs:
When hydatids are found in the liver, they can cause nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain. If occur in lung , there will be a lot of coughing leads to chronic cough, chest pain, and difficulty in breathing. Other indications depend on where the hydatid cysts are and how much pressure they put on the tissues around them. Anorexia, weakness and weight loss are all signs that aren’t very specific.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis made upon history and clinical signs and to confirm them laboratory tests are required. Different tests can be performed to identify hydatid cyst as
- Radiography
- Ultrasonography
- X-rays
- CT-Scan
- MRI
- Purging with arecoline hydrobromate
- Detection of antigen in feces through ELISA
- PCR
Treatment:
Surgery is the solution to remove hydatid cysts has become the most popular therapeutic option during the last couple of decades. Recent years, however, have seen the development of less invasive treatments, such as cyst puncture, aspiration of the fluid, injection of drugs, and subsequently re-aspiration of the liquids. In addition, benzimidazole based chemotherapy is a new treatment option for human as patients.
And frequent use of albendazole is seen effective in many cases.
Prevention:
Vaccines against anthelminthic parasites can be given to dogs. In the case of intermediate hosts, particularly sheep, these anthelminthic immunizations do result in an antigenic response, which means that the body generates specific antibodies against the parasite, but they do not prevent infection in the intermediate host itself. In order to avoid the propagation of this cestode to its definitive host, it is critical to perform a clean slaughter and maintain rigorous monitoring of any potential intermediate hosts during the slaughter process. After a home slaughter, the corpses and offal must be disposed of properly. Boiling livers and lungs that contain hydatid cysts for 30 minutes has been recommended as a simple, efficient, and energy- and time-saving method of killing the infectious larvae. It has been shown to be effective in several studies.
Author
1)Dr. Muhammad Rahman
DVM, M.Phil Parasitology
University of Agriculture, Faisalabad
m.rahmansaleem@gmail.com
2)Dr. Muhammad Sohail Sajid
Associate Professor, Department of Parasitology
University of Agriculture, Faisalabad
3)Dr. Hamid Ali Rana
Phd Scholar University of Agriculture, Faisalabad